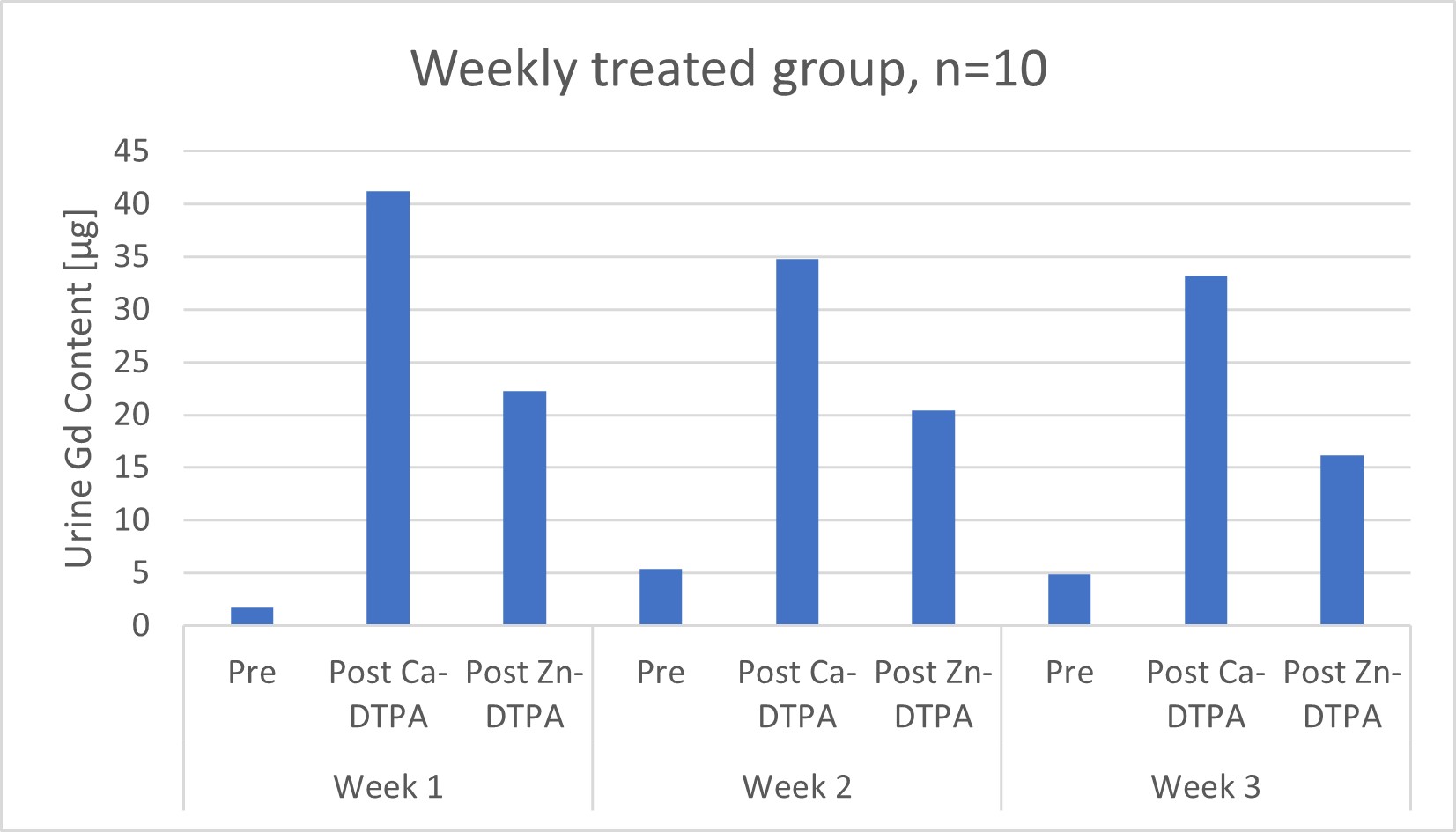
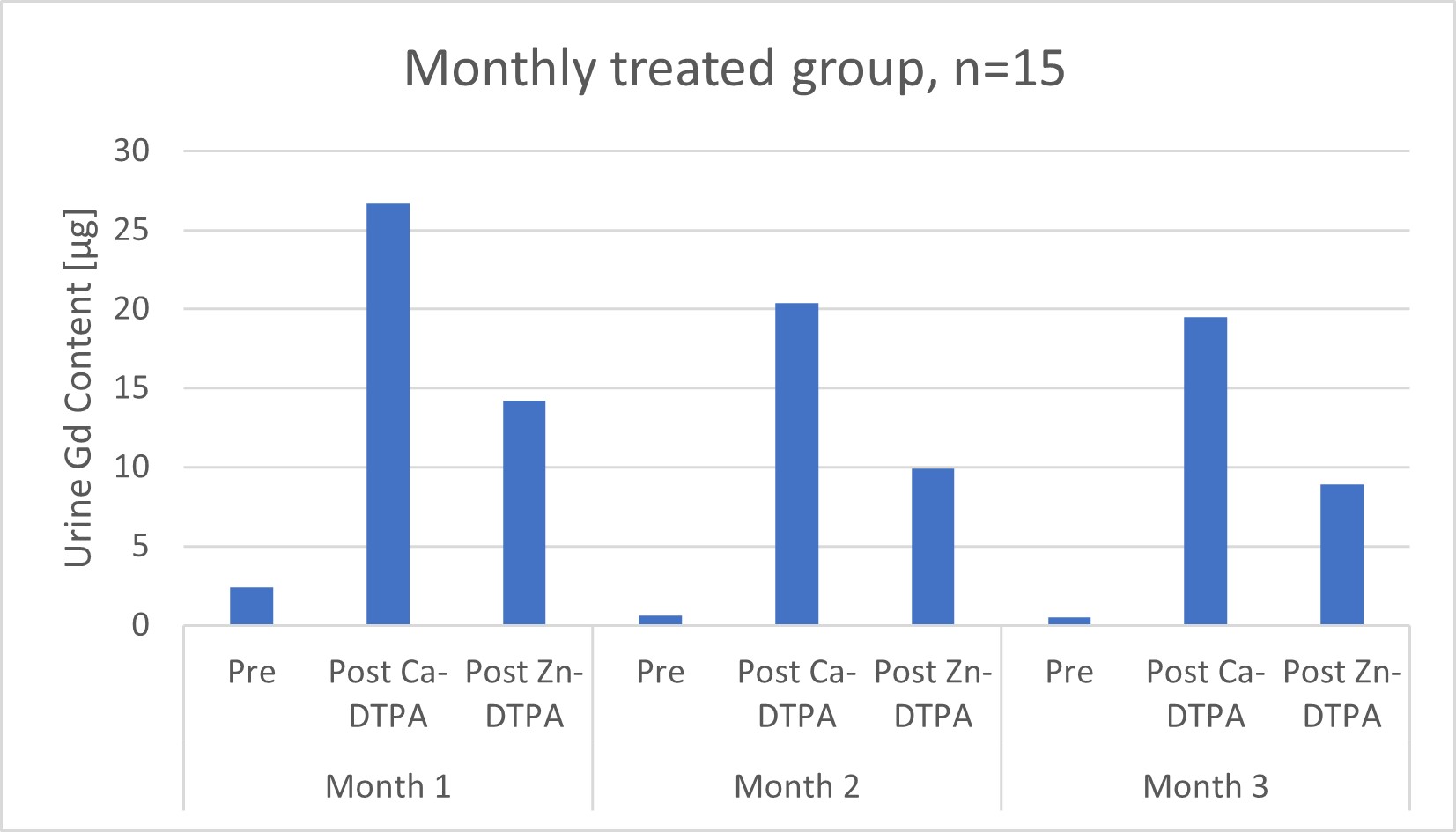
Study design: 25 symptomatic patients diagnosed with gadolinium deposition disease were treated 3 times with intravenous calcium (Ca)- and zinc (Zn)-diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid (DTPA) separated by 24 hours. Patients were divided into two groups; first group received treatments every month and second group received treatments every week. Before dosing and on the first and second day of therapy 24-hours urine gadolinium content was measured.
Results: In all patients 24-hour urine gadolinium content increased substantially after treatment with Ca- and Zn-DTPA.
Conclusions: Ca- and Zn-DTPA is able to increase the urine content of gadolinium, probably through transmetallation and recreation of a gadolinium-chelate (Gd-DTPA), which is eliminated with urine.