Study design: This retrospective study compared the expression of cancer stem cell surface marker CD44v9+ and proliferation of CD44+ cancer cells in patients treated with sulfasalazine in long-term or short-term therapy.
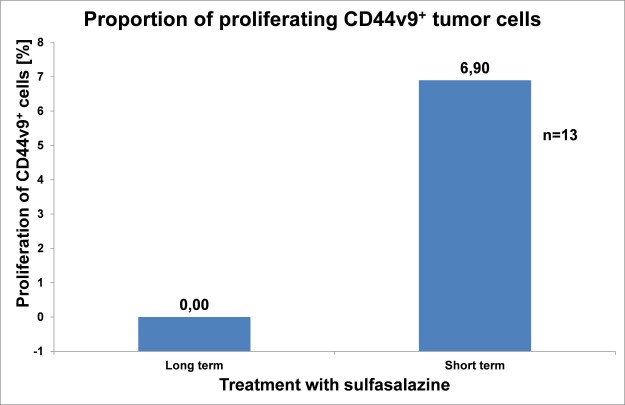
Results: CD44v9+ expression and median proportion of proliferating CD44v9+ were decreased in the long-term treated group compared to the short-term group as shown by immunohistochemical analysis.
Conclusions: Proliferation of CD44v9+ cells is reduced by long-term sulfasalazine administration, suggesting sulfasalazine as a new potential therapeutic agent targeting CD44v9+ cells.